Global Issues>>Environment:>> Climate Change >> Global Warming Global warming predictions prove accurateAnalysis of climate change modelling for past 15 years reveal accurate forecasts of rising global temperaturesMar 27, 2013 - Duncan Clark - guardian.co.uk
Predictions of rising temperatures due to human-induced climate change have proved accurate. Photograph: Graham Turner for the Guardian
The debate around the accuracy of climate modelling and forecasting has been especially intense recently, due to suggestions that forecasts have exaggerated the warming observed so far – and therefore also the level warming that can be expected in the future. But the new research casts serious doubts on these claims, and should give a boost to confidence in scientific predictions of climate change. The paper, published on Wednesday in the journal Nature Geoscience, explores the performance of a climate forecast based on data up to 1996 by comparing it with the actual temperatures observed since. The results show that scientists accurately predicted the warming experienced in the past decade, relative to the decade to 1996, to within a few hundredths of a degree. The forecast, published in 1999 by Myles Allen and colleagues at Oxford University, was one of the first to combine complex computer simulations of the climate system with adjustments based on historical observations to produce both a most likely global mean warming and a range of uncertainty. It predicted that the decade ending in December 2012 would be a quarter of degree warmer than the decade ending in August 1996 – and this proved almost precisely correct. The study is the first of its kind because reviewing a climate forecast meaningfully requires at least 15 years of observations to compare against. Assessments based on shorter periods are prone to being misleading due to natural short-term variability in the climate.
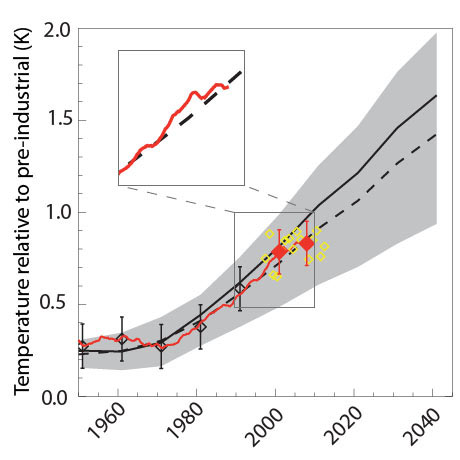
The climate forecast published in 1999 is showed by the dashed black line. Actual temperatures are shown by the red line (as a 10-year mean) and yellow diamonds (for individual years). The graph shows that temperatures rose somewhat faster than predicted in the early 2000s before returning to the forecasted trend in the last few years. Photograph: Nature Geoscience
The new research also found that, compared to the forecast, the early years of the new millennium were somewhat warmer than expected. More recently the temperature has matched the level forecasted very closely, but the relative slow-down in warming since the early years of the early 2000s has caused many commentators to assume that warming is now less severe than predicted. The paper shows this is not true. Allen said: "I think it's interesting because so many people think that recent years have been unexpectedly cool. In fact, what we found was that a few years around the turn of the millennium were slightly warmer than forecast, and that temperatures have now reverted to what we were predicting back in the 1990s." He added: "Of course, we should expect fluctuations around the overall warming trend in global mean temperatures (and even more so in British weather!), but the success of these early forecasts suggests the basic understanding of human-induced climate change on which they were based is supported by subsequent observations. |
Email this page to a friend
If you speak another language fluently and you liked this page, make
a contribution by translating
it! For additional translations check out FreeTranslation.com
(Voor vertaling van Engels tot Nederlands)
(For oversettelse fra Engelsk til Norsk)
(Для дополнительных
переводов проверяют
FreeTranslation.com )