The unit used in the graph is tce (tonnes of coal
equivalent). 1 tce = 29.3 GJ.
The unit used is tce (tonnes of coal
equivalent). 1 tce = 29.3 GJ.
The principal biomass resources in China are: (1)
residues from agriculture and forest
industries, (2) animal manure from medium
and large-scale livestock farms, and (3) municipal
solid waste.
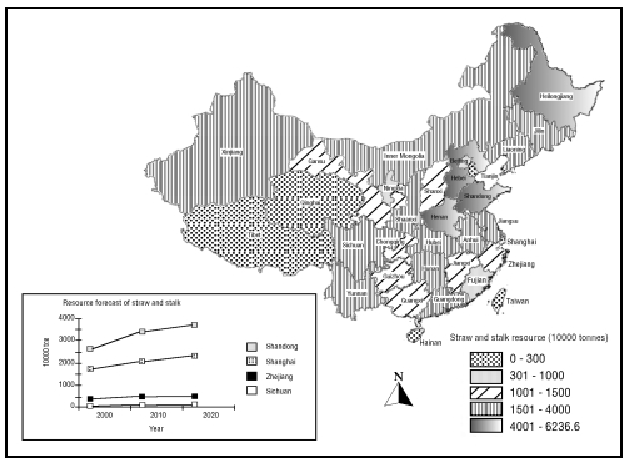
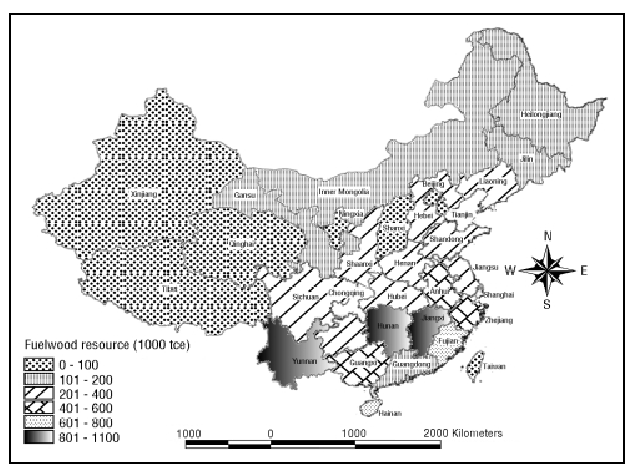
Agricultural and forestry residues Agricultural
and forestry wastes are the primary bioenergy resource
generated in China, as their production is related
to the main economic activity of a significant portion
of the country. Currently, less than half of these
wastes are used for some purpose, such as domestic
heating and cooking, fertilizer, animal forage,
raw material for paper, etc. The unused fraction
of the residues generally exceeds the amount needed
to maintain soil quality, and the field-burning
of the excess residues constitutes a growing environmental
hazard.
A main characteristic of this resource is that
it is usually spread across an extensive area, and
collection costs, especially for centralized use
of these wastes, can be high. Some activities, such
as sugarcane processing, involve a concentration
of the resource as part of the normal processing
activity and offer a clear opportunity for centralized
utilization. In general, biomass resources are widely
distributed and available in all regions of the
country.
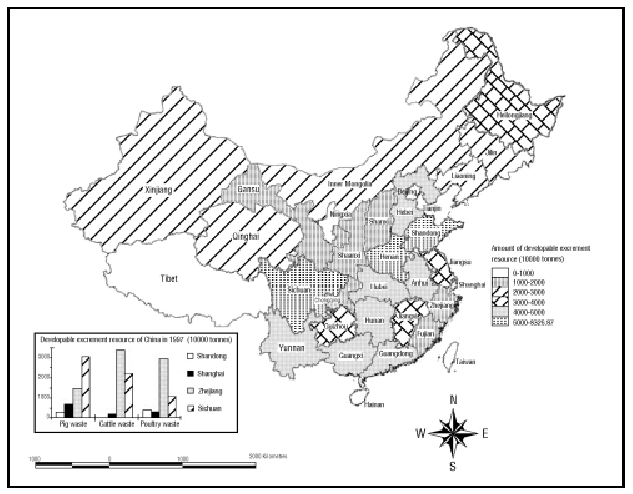
Livestock manure China has a long history of raising
many species of domestic livestock. There are generally
two methods of feeding. The traditional method,
natural feeding, is mainly suitable for small-sized
farms and families, and for specific animals, such
as sheep, horses and ducks. With this feeding method,
excrement is scattered in grasslands and pools and
thus difficult to collect. Concentrated feeding
at large and medium-sized farms for cattle, pigs,
sheep and poultry, has increased dramatically in
recent years. These livestock are generally reared
in pens so that the excrement can be easily collected.
The amount of this resource that can be utilized
depends on the manure collection efficiency as well
as the energy conversion efficiency. The electricity
potential is a modest 60.1 TWh.
Disposal of municipal solid waste (MSW) in China
reached nearly 300,000 t/day in 1995 and is expected
to continue to grow as China’s economy expands.
The energy content of the 1995 level of MSW is about
1230 PJ.
Afghanistan | Armenia | Azerbaijan | Bangladesh |
Bhutan | Brunei | Cambodia | China | Georgia |
India | Indonesia | Japan | Kazakhstan | Korea,
North | Korea, South | Kyrgyzstan | Laos | Malaysia
| Maldives | Mongolia | Myanmar (Burma) | Nepal |
Pakistan | Philippines | Singapore | Sri Lanka | Tajikistan
| Thailand | Turkmenistan | Uzbekistan | Vietnam |